侧边栏
这是本文档旧的修订版!
目录
Publications
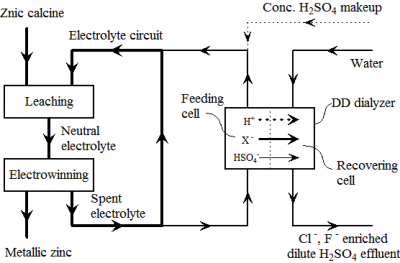
Selective removal of halides from spent zinc sulfate electrolyte by diffusion dialysis
J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, Pages 111–118 (1 September 2017)
By Hui-Fang Xiao, Qing Chen, Huan Cheng, Xiu-Min Li, Wen-Meng Qin, Bao-Sheng Chen, Dong Xiao, Wei-Ming Zhang*
j.memsci.2017.05.009, fulltext mmc1.xlsx
Zinc metal is mainly produced by a hydrometallurgical process, in which zinc electrolyte is recirculated, and impurities especially halides are accumulated then, which have dreadful impacts on the process and product. Until now numerous efforts have been made to remove halides from the electrolyte, but none of them are fully satisfying, and it is still a big issue for the industry. As a conventional membrane technology, diffusion dialysis (DD) is originally designed to recover free acid from acid-salt mixture by concentration gradient. In this work, we proposed a novel process to selectively remove these halide impurities from the spent zinc electrolyte by DD directly. Significant Cl- and F- permselectivities over HSO4- are observed in this process. The removal efficiencies are as high as 50–70% and 30–42% for chloride and fluoride, respectively, while the zinc loss is less than 1%. The flow intensity in the current work is much higher than that in conventional DD, which reduces the overall cost immensely. The mechanism of this selective mass transfer is also studied intensively to understand influence of flow intensity, charge number and hydrated radii of ions on the permselectivity. The results here are not confined to provide a superior method to remove halide impurities for the zinc industry, but also extend new applications and deepen understandings for the well-established DD process in selective ion separation. This capability is very likely to become a new growth point and future direction for the DD process besides acid/alkali recovery.
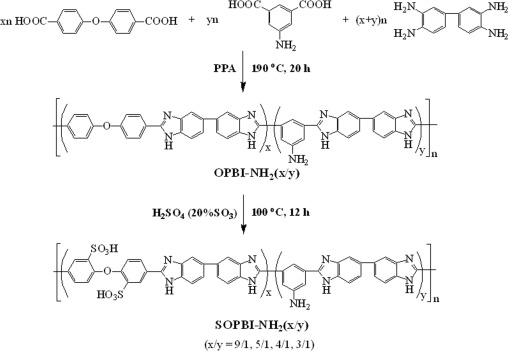
Preparation of covalently cross-linked sulfonated polybenzimidazole membranes for vanadium redox flow battery applications
J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, Pages 229–239 (1 March 2017)
By Zijun Xia, Libin Ying, Jianhua Fang*, Yu-Yu Du, Wei-Ming Zhang*, Xiaoxia Guo, Jie Yin
j.memsci.2016.10.050, local fulltext
A series of polybenzimidazole copolymers with varied content of pendant amino groups have been synthesized by condensation polymerization of 4,4′-dicarboxydiphenyl ether (DCDPE), 5-aminoisophthalic acid (APTA) and 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) in polyphosphoric acid at 190 °C for 20 h. The resulting copolymers undergo post-sulfonatation in fuming sulfuric acid at 100 °C yielded the highly sulfonated polybenzimidazoles (SOPBI-NH2(x/y), ‘x/y’ refers to the monomer molar ratio of DCDPE to APTA). A series of covalently cross-linked membranes (CSOPBI-NH2(x/y)) with good mechanical properties are fabricated by solution cast technique using bisphenol A epoxy resin as a cross-linker. The CSOPBI membranes show 3–4 orders of magnitude lower VO2+ permeability and 6–30 times higher ion diffusion selectivity (proton vs. VO2+) than Nafion117. The charge-discharge behaviors of the vanadium redox flow batteries (VRBs) assembled with the CSOPBI-NH2(x/y) membranes and Nafion 117 are investigated and compared. The VRBs assembled with the CSOPBI membranes exhibit significantly higher columbic efficiency and lower self-discharge rate than that assembled with Nafion 117 owing to the extremely lower vanadium cations crossover of the former. The VRB assembled with the CSOPBI-NH2(9/1) membrane exhibits fairly high energy efficiency (~85% at 60 mA cm−2) and little decay in performance is observed after 300 charge-discharge cycles.
Graphene enhances the proton selectivity of porous membrane in vanadium flow batteries
Materials & Design 2017, 113, pp 149–156 (5 January 2017)
By Qing Chen, Yu-Yu Du, Kai-Min Li, Hui-Fang Xiao, Wei Wang* and Wei-Ming Zhang*
j.matdes.2016.10.019, local fulltext
The vanadium flow battery (VFB) is one of the most promising technologies for large-scale energy storage, which has an enormous advantage in the stabilization and smooth output of renewable energy. As an essential separator in VFB, nanoporous membrane plays a key role in the final electrochemical performance, which requires both high H+ conductivity and low vanadium permeability. In this work, a novel graphene enabled porous membrane material has been successfully designed and fabricated by directly transferring several layers of graphene onto the surface of traditional polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane. The experimental results show that the graphene layers will impact the composite membranes performance in batteries. After three graphene single layers attached, the proton selectivity of membrane is significantly enhanced, and the overall battery efficiencies are improved by 10% at 20 mA cm− 2. Therefore, attaching graphene layers is a feasible and promising strategy to improve the performance of nanoporous membrane in VFB applications.
Acid blue 9 desalting using electrodialysis
J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, pp 28–36 (29 June, 2015)
By Chang Xue, Qing Chen, Yuan-Yuan Liu, Yu-Ling Yang, Dan Xu, Lixin Xue and Wei-Ming Zhang*
10.1016/j.memsci.2015.06.027, local fulltext
Currently nanofiltration predominates the membrane application of dye desalting and purification, and it is very effective to produce low-salt dye from raw dye with high inorganic salt impurities. However it is difficult and costly to produce dye products with ultralow impurities, because the desalting performance decreases proportionally as the concentration of salt impurity decreases. Here in this study, an optimized electrodialysis desalting process was proposed to fill the gap. The dye–membrane interactions, fouling mechanism and abatement strategy were carefully investigated and well understood. Long term system performance stability and reasonable process cost are achieved. Nearly all SO42− in the feed dye can be removed, and residual [Cl−] is only 130 mg/L (~96% removal) in the final aqueous dye product (~200 g/L). The overall purification cost is $0.097/kg as dye solids, which is very economically competitive. The electrodialysis desalting process proposed here provides another feasible and competitive approach for dye desalting and purification other than nanofiltration.
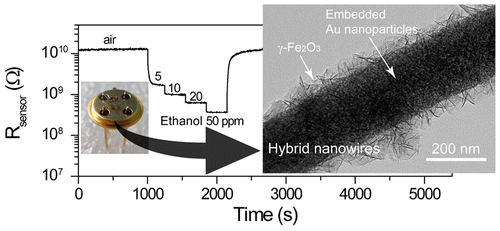
Gold Embedded Maghemite Hybrid Nanowires and Their Gas Sensing Properties
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7 (19), pp 10534–10540 (May 4, 2015)
By Na-Mei Li, Kai-Min Li, Shun Wang, Ke-Qin Yang, Li-Jie Zhang, Qing Chen* and Wei-Ming Zhang*
10.1021/acsami.5b02087, local fulltext
Well-defined gold embedded maghemite hybrid nanowires are synthesized, and their structures are fully characterized. They are composed of porous γ-Fe2O3 shells and embedded gold nanoparticles (3–10 nm), which is novel and very different from the conventional “surface decoration” configuration. These hybrid nanowires are produced by the de-alloying of Au–Fe alloy nanowires and subsequent heat treatment. The reaction mechanism is proposed and validated. The results of X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and thermogravimetry techniques prove consistently that the Fe composition of Au–Fe alloy nanowires change to γ-FeOOH first and then to γ-Fe2O3. The embedded gold particles are help to enhance the gas response properties of the hybrid nanowires, which is attributed to the nano open-circuit Schottky junctions between γ-Fe2O3 and the Au nanoparticles. The gas sensing experiment data with high repeatability demonstrate that these hybrid nanowires are excellent sensing materials, especially for ethanol, and have shown both high selectivity and high sensitivity.
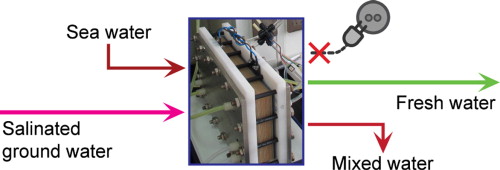
Energy self-sufficient desalination stack as a potential fresh water supply on small islands
Desalination, 2015, 359, pp 52–58 (2 March, 2015)
By Qing Chen, Yuan-Yuan Liu, Chang Xue, Yu-Ling Yang and Wei-Ming Zhang*
10.1016/j.desal.2014.12.010, local fulltext
Sea water intrusion causes fresh water shortage on small islands, and desalination systems are needed to desalt the salinated water (brackish water) and produce fresh water. Unfortunately conventional desalination technologies can only work properly with stable external power inputs, which are usually not accessible in these rural areas. In this study we propose an integrated self-desalination stack that consists of alternate anion and cation ion exchange membranes and couples the technologies of reverse electrodialysis and electrodialysis. The salinity gradient energy between sea water and brackish water is harvested to demineralize another portion of brackish water directly in the same stack. The overall process is spontaneous and energy self-sufficient with minimum peripheral devices, and it is promising to provide fresh water supply especially for these rural residents on small islands.
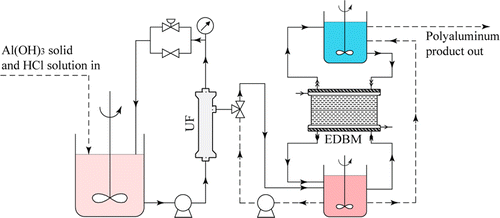
Green Production of Ultrahigh-Basicity Polyaluminum Salts with Maximum Atomic Economy by Ultrafiltration and Electrodialysis with Bipolar Membranes
Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53(34), pp 13467–13474 (18 August, 2014)
By Qing Chen, Chang Xue, Wei-Ming Zhang*, Wei-Guo Song*, Li-Jun Wan, and Kun-Song Ma
10.1021/ie5023546 local fulltext
Ultrahigh-basicity polyaluminum, an important aluminum industrial product, is manufactured by the oxidation of metallic Al with acids. The process is not economically and chemically efficient because the aluminum atoms were reduced first from alumina to aluminum metal and then oxidized again to get the polyaluminum. In this work, an integrated synthesis system has been built to produce ultrahigh-basicity polyaluminum salts, including polyaluminum chloride, sulfate, and nitrate, from aluminum hydroxide and corresponding acids directly at normal temperature and pressure. Ultrafiltration and electrodialysis with bipolar membranes work in tandem during the synthesis. Aluminum salts are produced naturally from aluminum hydroxide solids and acids in a mixing tank, which are separated as pure solutions via ultrafiltration and then basified in an electrodialysis stack with bipolar membranes to get polyaluminum and regenerate acids as byproducts. These acids are sent back to the mixing tank for reuse again. This integrated system works with maximum atomic economy and low overall cost, which makes it a green process for the production of polyaluminum salts.
基于膜分离的电极箔行业减排降耗过程研究
By 陈庆 张伟明
水处理技术 2014, 40(3), pp 44-48 (Mar. 2014)
出版社链接 全文
提出了一种基于膜分离技术的新思路来解决电极箔行业在生产过程中所产生的大量腐蚀废酸及清洗废水的排放问题,这些工业废液中的资源可以被分离出来并得到重复利用。通过系统集成,笔者利用扩散渗析及双极膜电渗析联用技术,实现了行业腐蚀废酸零排放的回收处理;同时借助频繁倒极电渗析技术,还实现了己二酸铵清洗废水中药剂及纯水资源的回收。实验结果表明,这些新过程的开发有望改变电容箔行业高消耗、高污染的现状,大大减少社会资源消耗总量及污染物排放总量,实现行业可持续发展。
关键词: 电极箔 膜分离 扩散渗析 电渗析 双极膜 腐蚀废酸 清洗废水 回收
Zero discharge process for foil industry waste acid reclamation: Coupling of diffusion dialysis and electrodialysis with bipolar membranes
J. Membr. Sci., 2013, 432, pp 90–96 (1 April, 2013)
By Jin-Xia Zhuang, Qing Chen, Shun Wang, Wei-Ming Zhang*, Wei-Guo Song*, Li-Jun Wan, Kun-Song Ma, Chun-Nian Zhang
10.1016/j.memsci.2013.01.016
local fulltext
A zero discharge process was proposed to totally recover both acid and aluminum resource from the waste acid in foil industry. Diffusion dialysis (DD) was coupled with electrodialysis with bipolar membranes (EDBM) in this process, in which most of the free acid was first recovered by DD; and the resulting waste dialysate was further basified by EDBM, recovering aluminum resource and the rest of free acid. Through this process, all components in waste acid were recovered as valuable chemicals, resulting in zero discharge of dangerous effluents. This process is profitable in terms of cost analysis and significantly reduces the environmental burden of foil industry, enabling the foil industry to be more cost-effective, more environmental friendly and more sustainable.
Cost-Effective Production of Pure Al13 from AlCl3 by Electrolysis
Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2012, 51 (34), pp 11201–11206 (17 August, 2012)
By Wei-Ming Zhang*, Jin-Xia Zhuang, Qing Chen, Shun Wang, Wei-Guo Song*, and Li-Jun Wan
10.1021/ie301048k,
local fulltext
An integrated electrolysis system was built to synthesize polyaluminum chloride with ultra high-basicity and even pure Al13. The system converts AlCl3 solution from aluminum electrode foil industry waste to Al13 chloride directly with reasonable cost, typically $1.09 per kilogram as Al2(OH)5Cl·2H2O at 25 °C. Electrolyte temperature and current density were investigated to optimize the process. Ferron assay and 27Al NMR results indicated that the purity of Al13 is over 99% in product solutions. Ion chromatogram analysis confirmed that Cl– ions accounted for about 96.5% in all counteranions. Our integrated system is the first instance to obtain pure Al13 polycations directly. Similar high purity products are only available after tedious purification. This effective and economic synthesis procedure has potential for mass production of Al13 for water treatment and catalyst as well as cosmetic industries.